Smart Green Infrastructure
With Argonne National Lab and researchers across McCormick engineering departments (Aaron Packman, George Wells, Jennifer Dunn, Bill Miller and others) we have been exploring how sensors, computing systems, and artificial intelligence / machine learning can be applied to critical problems in sustainable urban systems. We have been exploring novel energy supplies for ultra long term sensing, and how large scale sensor infrastructure can be enhanced to provide ways for citizens to engage in the scientific process and support resilient cities and coastlines.
This project is located at Northwestern University and sponsored by the National Science Foundation under award #2038853
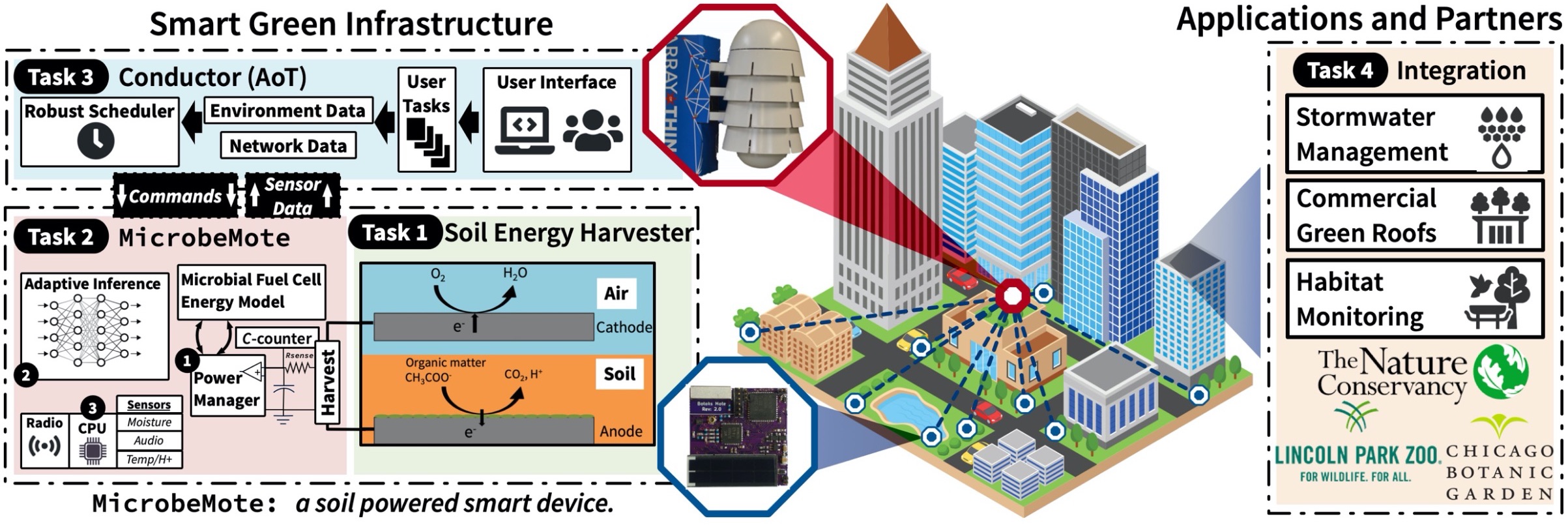
Cities across the nation have invested significantly in making infrastructure smarter, more sustainable, and more resilient to extreme weather events. Green infrastructure (GI), a general term for planned installations of trees, plants, soils, wetlands, and other natural resources, is increasingly being installed in cities nationwide to provide resilience to flooding, sewer overflows, urban heat, air pollution, habitat loss, and coastal erosion, that are overwhelming traditional infrastructure and negatively impact urban life. Embedding smart devices in GI provides numerous benefits to a city, providing insight into the health and effectiveness of the system, and the operations and fitness of the city. However, deploying smart devices in GI is challenging because of the scale and need for long-term deployment, meaning battery-powered or expensive plugged-in devices are not feasible. This project builds Smart Green Infrastructure; augmenting GI with battery-free smart devices, powered by energy harvested directly from soil, which gather data, infer, actuate, and collaborate with each other. By harvesting from freely available soil and removing batteries, these devices can last for decades. Through partnerships with organizations in Chicago, Illinois–The Nature Conservancy, the Chicago Botanic Garden, and the Lincoln Park Zoo–the project demonstrates applicability by tackling stormwater management, urban wildlife surveillance, green roofs and other real-world applications. . Beyond cities, the work in this project will enable new applications in agriculture and smart farming, water resources management, and any applications where long term, zero maintenance embedded intelligence is required.
Building Smart GI presents cyber-physical systems challenges in enabling robust inference, communication, and coordination on ultra-constrained computing platforms, and despite frequent power failures and dynamic energy availability. These devices harvest energy from soil or plant organic matter using terrestrial Microbial Fuel Cells (MFCs), constructed from inert materials providing decades long lifetime. These devices use machine learning to understand their environment, enabling robust, long-term monitoring that requires no maintenance or replacement. Finally, these devices actuate to “heal” the surrounding environment, switching the MFC from energy generation, to producing a disinfectant instead with the microbial community. A high-powered edge device orchestrates the actions of the swarm of MFC powered nodes, making decisions based on network data and external factors like user tasks. Project tasks include; co-design of the Terrestrial MFC and corresponding energy model for efficient and dynamic energy harvesting and; development of a tiny, resilient computing platform that harvests soil energy and supports sensing, and actuation; creation of a framework for conducting on-device machine learning to recognize subtle environmental changes from lossy data; exploration of orchestration of a network of intermittently powered devices; and conducting a series of end-to-end deployments with Chicago institutions.
Indigenous Led Cyberinfrastructure
The Northwestern University campus sits on the ancestral homelands of the people of the Council of Three Fires: the Ojibwe, the Potowatomi, and Odawa, as well as the Menominee, Miami, and Ho-Chunk Nations.
An interdisciplinary team of researchers including PI Hester and Northwestern Engineering faculty has been awarded a grant to address challenges faced today by the Ojibwe Nations.
As part of the Civic Innovation Challenge, led by the US National Science Foundation (NSF) in partnership with the US Department of Energy and US Department of Homeland Security, the team received $50,000 in funding for its project, “Strengthening Resilience of Ojibwe Nations across Generations (STRONG): Sovereignty, Food, Water, and Cultural (in)Security.”
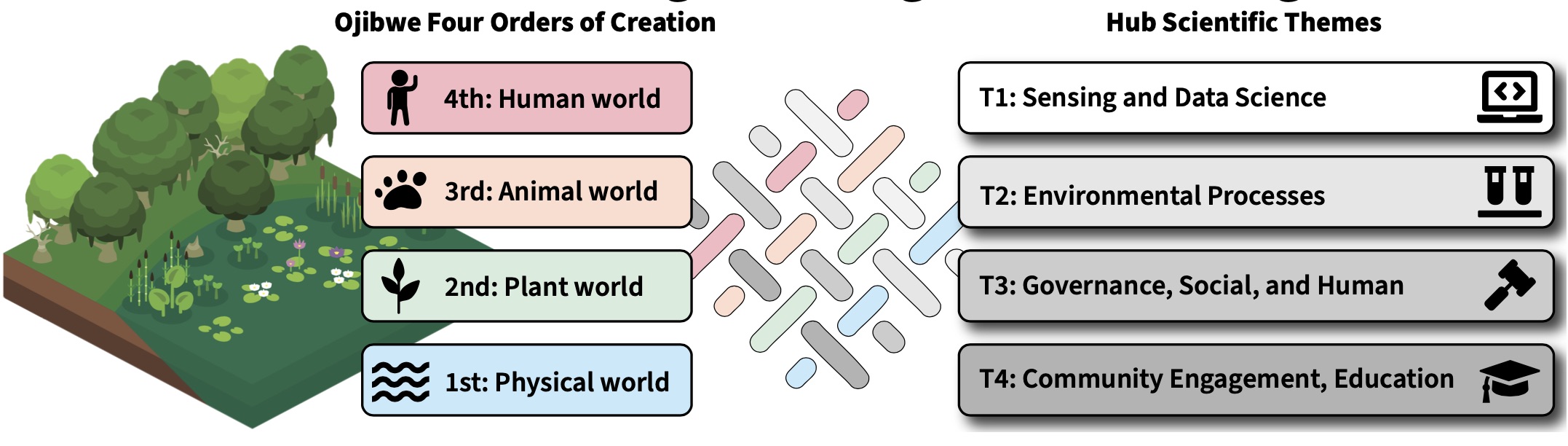
The project’s vision is to co-create methods with Ojibwe communities that integrate traditional ecological knowledge with data science, environmental science, social science, and engineering platforms to strengthen future Ojibwe generations’ resilience. Using a sovereignty-affirming approach that advances cultural, food, and water security, the researchers will co-develop monitoring, prediction, and response systems and decision-making tools for strengthening resilience to natural disasters and other environmental threats. See our summary video starting at nine minutes, below.
Coastlines and People Hub: Manoomin
We participated in the CIVIC inovation challenge, and have continued our work with Ojibwe nations building cyber infrastructure, including proposing a new Coastlines and People Hub.
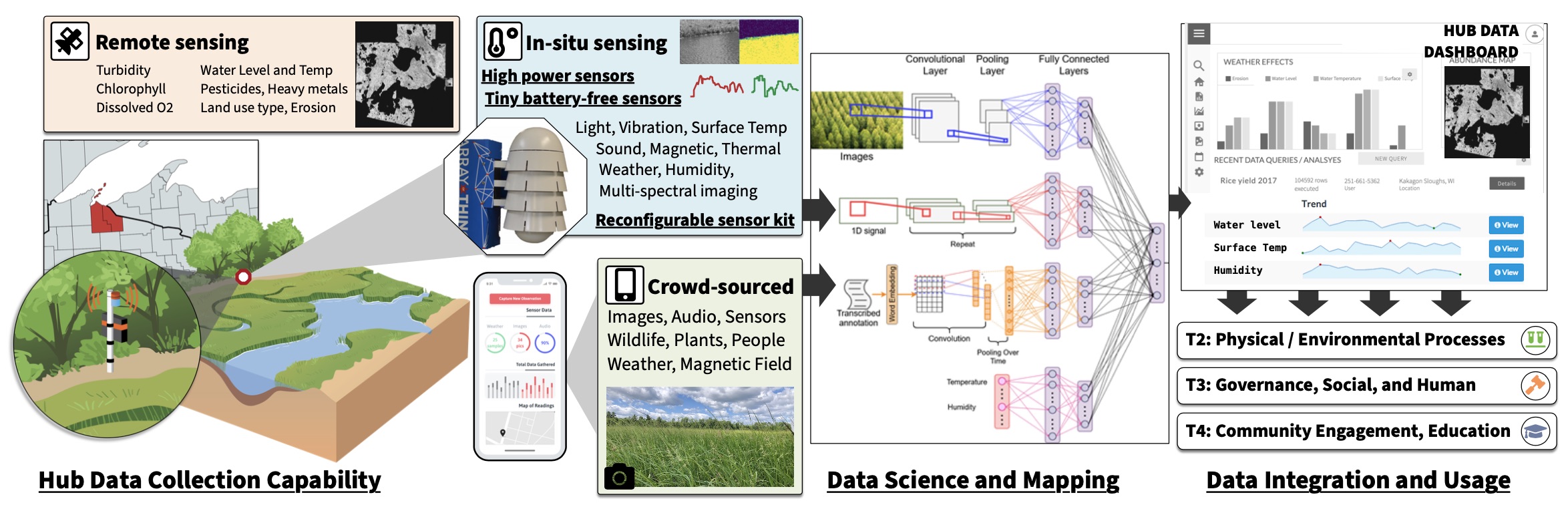
The Hub Vision is to develop cyber, scientific, and community foundations to ensure 7th generation sustainability of the Western Great Lakes. We bring together tribes, conservationists, and researchers around manoomin (wild rice) as a pillar of Ojibwe culture and livelihood, and as a keystone sentinel species for understanding and conserving Great Lakes coastal wetlands.